Bio-fertilizer Production Technology
Why Is Bio-fertilizer Favored by Many Fertilizer Factories?
Bio-fertilizer, is a product that contains both nutrient elements required by crops and microbes, and is a combination of biological, organic, and compound matter. It can be used in place of chemical fertilizer and provides all of the nutrients required for plant growth and development.
Bio-fertilizer has a long-lasting effect, improves the utilization rate of fertilizer, reduces agricultural production costs, increases output and income, improves product quality and soil, and reduces environmental pollution. It is the ideal fertilizer for pollution-free agricultural production and organic agricultural production, and has broad development and application prospects in sustainable agricultural development.
New Bio-fertilizer Production Technology And Process
Why Many Fertilizer Plants Apply Our Bio-fertilizer Production Technology?
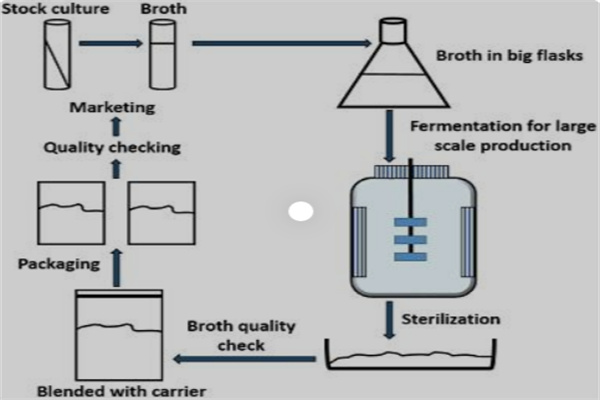
- The general traditional bio-fertilizer production process is: strain preservation → culture medium & activation → liquid fermentation → packing by using physical adsorbents or dilution method in a certain proportion.
- The construction of such a manufacturing plant involves the establishment of a bioclean room, air compressor, fermentation pot and filter. It is difficult to control culture and fermentation conditions, as well as the quality of strains with large investment and cost.
The bio-fertilizer production technology adopted by our company requires the addition of microbial agents that promotes the decay and decomposition of organic materials during the fermentation process, as well as achieve the purpose of deodorization. Besides, bacteria added in the post-treatment process with specific functions can enhance the effect of finished products. This is an excellent option for small and medium scale fertilizer producers, particularly generating bio-organic and inorganic fertilizer.
Bio-fertilizer Production Technique
Most bio-fertilizer production enterprises employ the groove type fermentation method. Moreover, other fermentation methods like windrows composting method and seal pot fermentation method, also occur in the bio composting process.
- Notes:
- The adjustment of moisture, C/N ratio, temperature, and the use of microbial agent is the key to the production process. In particular, the application of microbial agent directly affects the cycle of fermentation and the degree of decomposition of materials.
- The composted product basically realize the harmless production, which is also conducive to the survival of the functional bacteria added in the post-treatment procedure.
During the post-treatment, most enterprises add functional bacteria for rebatching, and the products are mainly in powder form, but some companies apply roller granulation or extrusion granulation.
- Note:
- Granular products overcome the shortcomings of poor appearance of powder products and improve the commodity of the products.
- Nevertheless, it also increases the production cost of enterprises and has a certain impact on the survival of effective bacteria.
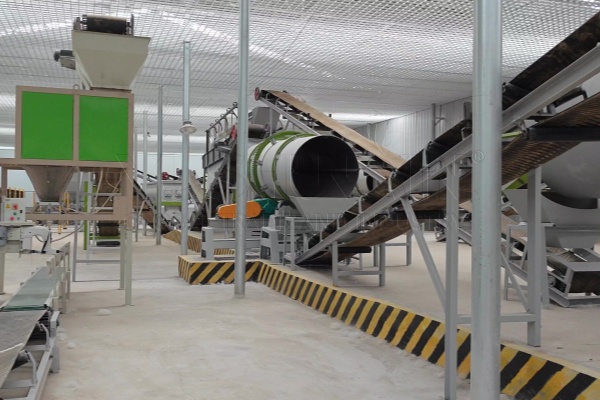
Specific Process Flow
There are three basic types of bio-fertilizer manufacturing processes:
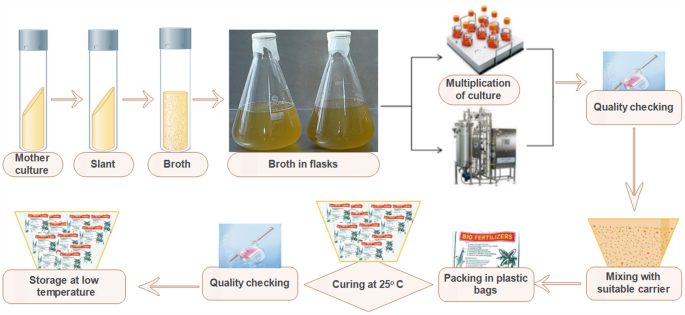
After expand culture, microbes with specific functions (e.g. rhizobium, potassium bacteria, phosphate solubilizing bacteria, etc.) combine with microcarriers (like grass charcoal or vermiculite) to make inoculants for small scale production.
Working Flow:
Microbial strains fermentation → Physical adsorbents (e.g. grass charcoal and zeolite) → Mixing in certain proportion → Crushing → Microbial Agent
Microbes are mixed with organic matter, such as animal manure, grass charcoal and brown coal.
Working Flow:
- Dewatering (e.g. manure) → Crushing → Screening → Mixing (microbial agents, organic waste and straw) → Composting → Screening → Packing/Granulation production line → Packing
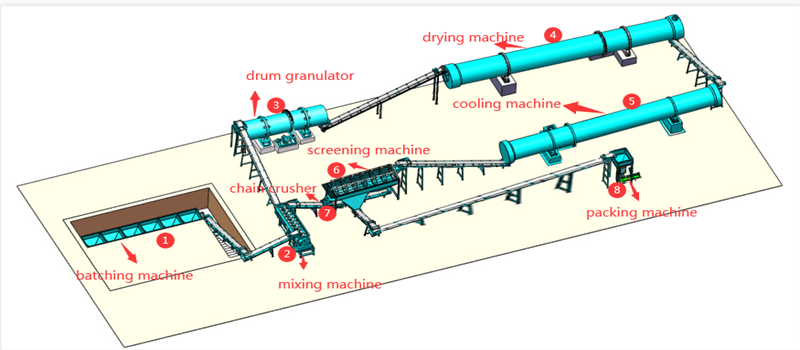
Microbes are mixed with inorganic matter (e.g. chemical fertilizers and micronutrients) to make the base fertilizer and the topdressing for large scale production.
Working Flow:
- Batching (NPK) → Mixing with bacteria → Granulating → Drying & Cooling → Screening → Packing
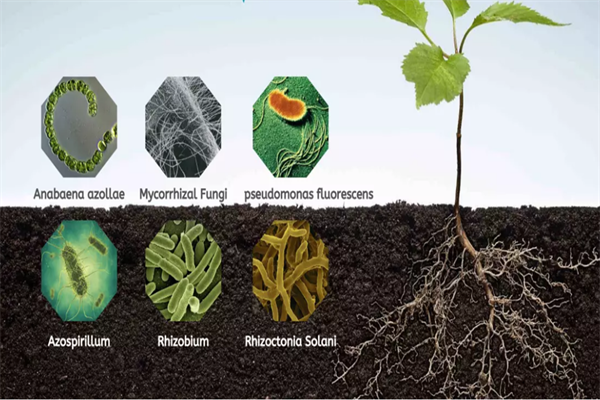
What Species of Bacteria Can Use in Bio-fertilizer Production?
Microbial strains are the core of bio-fertilizer products, which are generally used in two parts during the production process.
- Adding microbial agents in the composting process is to achieve the function of decomposition and deodorization. They mostly contains compound bacteria, such as photosynthetic bacteria (PBS), lactic acid bacteria (LAB), saccharomycetes, actinomycetes, penicillium, trichoderma, etc.
- The functional bacteria are added to the semi-finished products during the post-treatment, like nitrogen-fixing bacteria, phosphate solubilizing bacteria, silicate bacteria, lactic acid bacteria, pseudomonas or actinomycetes, play a specific effect in fertilizer production.
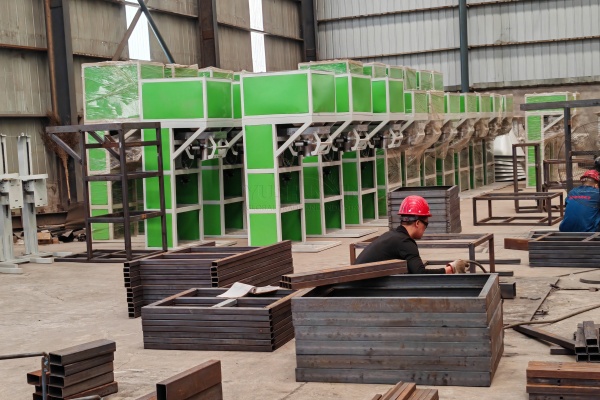
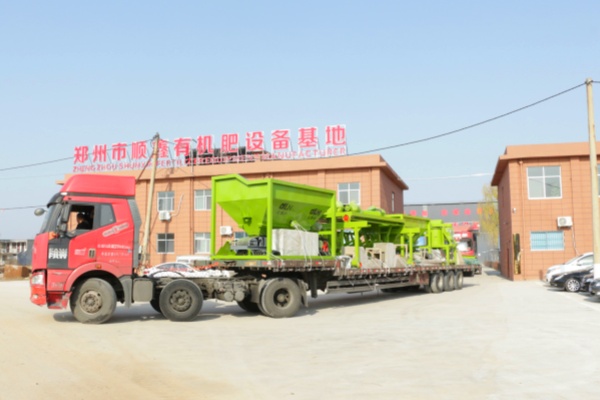
Bio-fertilizer Production Equipment
- 1
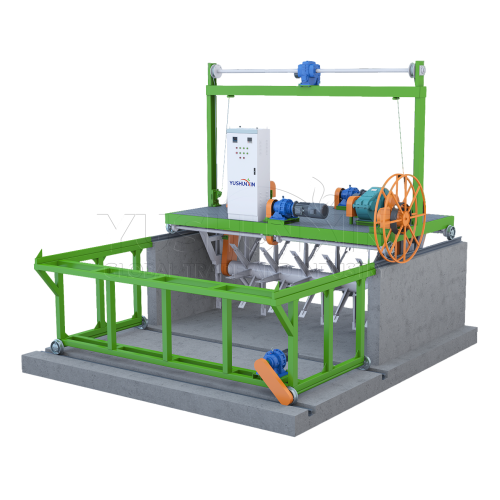
Composting: Groove type compost turner, moving type compost turner, organic fertilizer fermentation pot, etc.
- 2
Batching: Static batching machine and dynamic automatic batching system, loader type feeder, etc.
- 3
Crushing: New type vertical crusher, semi-wet material crusher, straw crusher, etc.
- 4
Mixing: Horizontal mixer, disc mixer, single shaft mixer, BB fertilizer mixer, etc.
- 5
Granulating: Disc granulator, rotary drum granulator, flat die granulator, new type organic fertilizer granulator, organic fertilizer polishing machine, etc.
- 6
Other Auxiliary Equipment: Dryer and cooler, rotary screening machine, conveying machine, rotary coating machine, the automatic quantitative packing scale, automatic palletizer, dust collector, etc.
Quality Bio-fertilizer Made by Our Production Technology!

Get Free Quote Now!